
What is Predictive Maintenance? 2024 Summary
Industries have to re-evaluate and re-interpret their maintenance and production processes in line with the digitalization experienced in the last 10 years. This rapid change and transformation are forcing production facilities to be smarter and more competitive. Industrial maintenance now has to be as digital and smart as possible for production facilities. Predictive maintenance offers great opportunities to businesses for a smarter and more digital facility. In our new article, let’s take a look at what predictive maintenance is, why it is used, what advantages it provides to businesses.

What is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is a technique that uses data analysis tools and techniques to detect anomalies in your operation and potential defects in equipment and processes. Thanks to predictive maintenance, possible failures are detected in advance and possible errors are prevented. This way, production facilities have a chance to reduce unplanned downtime as much as possible. While techniques such as oil analysis, vibration analysis, and infrared were frequently used in predictive maintenance in the past, predictive maintenance technologies have also changed and developed with the cheapening of sensors and the spread of IoT technology. For more information condition monitoring.
How does Predictive Maintenance work?
Predictive maintenance utilizes sensors and devices that connect wirelessly to a system. These sensors monitor factors, like temperature, vibrations and oil levels to provide real time information on equipment performance.
Data Analysis
The data gathered from sensors is sent to a hub where machine learning algorithms analyze it within the context of machine operation and wear. This analysis helps detect patterns, anomalies and deviations from operating conditions.
Predictive Models
Predictive maintenance models utilize the gathered data to predict equipment failures. Suggest maintenance actions. These models compare equipment behavior with expected behavior enabling technicians to take action before breakdowns occur. Early detection aids in preventing failures and reducing downtime.
Establishing a Predictive Maintenance Plan
For a predictive maintenance plan implementation businesses should consider the steps;
Start small; Initiate predictive maintenance on select assets before expanding. This approach allows testing of the strategys effectiveness and refining the process.
Identify assets; Determine which assets are most suitable, for maintenance.
Certain equipment may have importance. Be more susceptible, to breakdowns, which makes them suitable candidates for this method.
Resource allocation; Identify the resources needed for implementing maintenance, such as manpower, materials, infrastructure and technology. Providing training to staff involved in the procedure is also crucial.
Initiate asset monitoring; Begin monitoring the selected assets and gather data. This data serves as the basis for establishing a maintenance system.
Create machine learning algorithms; Utilize the gathered data to create personalized machine learning algorithms of forecasting equipment failures based on data trends.
Implement algorithms on trial assets; Apply the algorithms to trial assets. Produce reports and insights derived from the collected data. This stage enables companies to assess the efficiency of their maintenance regimen.
Continuous enhancement; Utilize outcomes and input from trial assets to enhance and optimize the maintenance process. Continuous improvement guarantees that the strategy remains effective, over time.
What Does Predictive Maintenance Offer to Factories?
Decrease in maintenance costs
Predictive maintenance is essential when creating a comprehensive maintenance management program for an industrial facility. While traditional maintenance programs are based on service routines for all equipment and offer rapid response to unexpected failures, predictive maintenance plans specific maintenance tasks only when they are actually needed. Therefore, one of the leading benefits of predictive maintenance is the reduction of overall maintenance costs in the business. Predictive maintenance reduces the cost of spare parts, tools and other equipment required for equipment maintenance.
Decrease in machine breakdowns
Regular monitoring of the actual conditions of equipment and process systems significantly reduces the number of unexpected and catastrophic equipment failures. When comparing the unexpected equipment failure prior to the implementation of the predictive maintenance program and the two-year period following the inclusion of condition monitoring into the program, the failure rate drops significantly.
Decrease in Stock Costs
The ability to predict defective parts and tools that require repair and the relevant workmanship skills reduces both repair time and costs. Industrial facilities have sufficient time to order a replacement or spare parts as needed, rather than purchasing all spare parts for stock.
Better Production Efficiency
The availability of process systems increases after implementing a state-based predictive maintenance program. The improvement here is based on machine availability and does not include improved process returns. However, a complete predictive maintenance program that includes process parameter monitoring contributes significantly to production efficiency.
Increased Employee Safety
Early warning of machine and system problems reduces the risk of catastrophic failure that could result in personal injury or death.
Longer Service Life
Prevention of catastrophic failures and the early detection of machine and system problems increase the service life of industrial machines by an average of 30%. Another benefit of predictive maintenance is that it can automatically estimate the mean time between failures (MTBF). This statistic provides a way to determine the most cost-effective time to replace the machine rather than constantly incurring high maintenance costs.
Verification of Maintenance Activities
Predictive maintenance can be used to determine whether repairs made on existing machines fix the identified problems or cause additional abnormal behavior before the system restarts. In addition, the data obtained in the predictive maintenance program can be used to schedule plant shutdowns. Many industries try to fix major issues or schedule preventive maintenance schedules during annual maintenance shutdowns. Predictive data can provide the information necessary to schedule specific repairs as well as other activities during shutdown.
What is the Difference Between Preventive and Predictive Maintenance?
Preventive maintenance involves the inspection and maintenance of an asset at predetermined intervals, whether necessary or not. Maintenance intervals are typically based on usage or time determined from the average life cycle of an asset. Predictive maintenance ensures consistent tracking of an asset, which helps to define a tailored maintenance plan for each asset. This approach maximizes an asset’s lifetime while at the same time contributing to lowering maintenance costs.

The main difference between preventive and predictive maintenance is that preventive maintenance is scheduled regularly, whereas predictive maintenance is scheduled based on asset conditions, i.e., is scheduled only when needed. Thus, predictive maintenance reduces labor and material costs, whereas preventive maintenance costs less to implement. But implementing a predictive maintenance program requires a vast amount of money, training, and resources upfront. These costs are often acceptable to organizations that have already successfully implemented a preventive maintenance program.
Preventive maintenance faces the challenge of balancing the cost with returns. Experienced maintenance managers need to make smart decisions about the requirement of preventive maintenance tasks and how much they should be done.
| Predictive Maintenance | Preventive Maintenance |
| It is performed to predict failures that might occur. | It is performed to prevent assets from unexpected failures. |
| It is done on a regular basis. | It is done on a regular basis. |
| No downtime of machine is required, i.e. one does not need to stop main functions of assets as this maintenance can be performed while assets are performing their regular functions. | One needs to increase downtime of the asset to carry out maintenance, i.e. one needs to stop main functions of assets to carry out maintenance action. |
| Maintenance occurs only when potential failures are identified. | Maintenance occurs even if potential failures are not identified. |
| It is more complex and difficult than preventive maintenance. | It is a less complex process and simple than predictive maintenance. |
| This maintenance action is less costly than preventive maintenance as one can simply reduce avoid maintenance that is not necessary and thus reduce maintenance costs. | This maintenance action is more costly than predictive maintenance, as regular maintenance requires more investment. |
| It is less time-consuming as in this type of maintenance, one needs to perform inspection and maintenance only when required. | It is more time-consuming because in this type of maintenance one needs to perform inspection and maintenance regularly. |
How Artesis Helps You?
Thanks to its comprehensive fault detection feature, Artesis Predictive Maintenance solutions significantly reduce your maintenance costs and contribute to your energy efficiency throughout the facility. The error detection accuracy is higher than 90%, ensuring the most accurate maintenance.
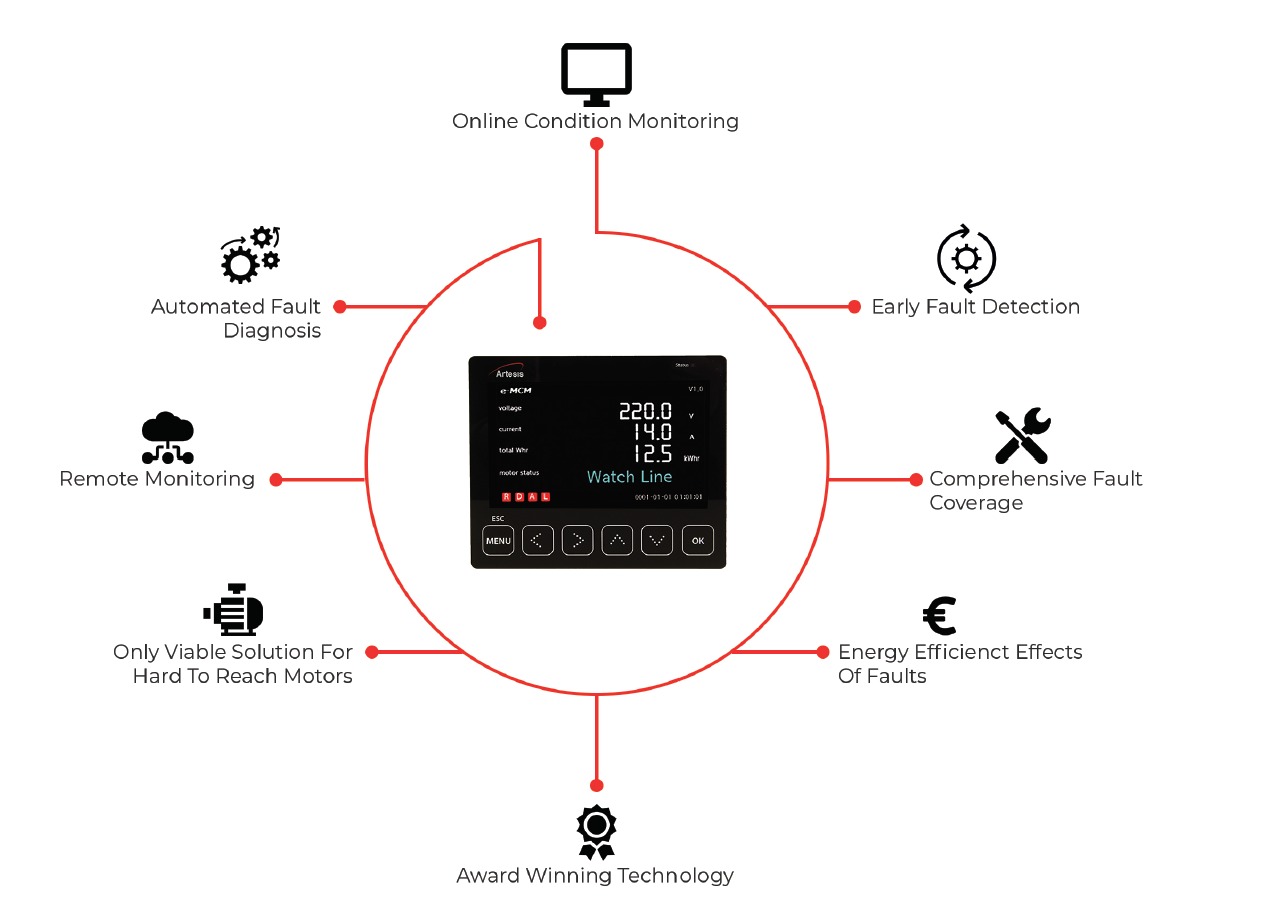
Easy Installation
e-MCM installation requires only three-phase voltage and current connection via low-cost current transformers (CT) and voltage transformers (VT) (if needed). It is usually located at the motor control cabinet, requiring very short cable runs and avoiding the need to install equipment in remote or hazardous areas.
Easy Use
Predictive maintenance enables automatic database establishment and monitoring of parameters. The degree of failure is displayed on a variable scale, eliminating the need for expert personnel.
Diagnostic
Predictive maintenance is effective in detecting electrical, mechanical and process faults. In addition, it can be used in both production and energy efficiency measurement. This point is important, since studies show that motor failures can affect energy efficiency up to 18%.
Early warning
In Motor Condition Monitoring technology, threshold values are not affected by system conditions. Therefore, predictive maintenance can give early and accurate warnings.
Future of PdM
The future of maintenance is bright, with advancements and wider acceptance anticipated. As technology progresses the challenges associated with implementation are likely to decrease making predictive maintenance more accessible and cost effective for businesses of all sizes.
Companies that embrace maintenance practices stand to gain from operational efficiency cost savings and improved maintenance strategies. Predictive maintenance is set to play a role in industries ensuring the longevity and peak performance of essential equipment.
In summary predictive maintenance enables businesses to adopt an approach to maintenance through the use of technology and data analysis. By detecting equipment issues before they manifest companies can reduce downtime cut expenses. Prolong the lifespan of their machinery. With technology advancing the future of maintenance appears promising emphasizing its importance, for businesses striving to remain competitive in an ever evolving environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is a technique that uses data analysis to detect errors that may occur in your operations and equipment in advance. Thanks to predictive maintenance, it is aimed to prevent unplanned downtime.
What are the advantages of predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is one of the most important factors that increase productivity in the facility. Direct benefits of predictive maintenance include early detection of equipment failure, analysis of root causes, improved productivity, employee safety, reduction of resources.
What is the difference between predictive and preventive maintenance?
The difference between preventive maintenance and predictive maintenance is the data analysed. The data of the equipment running in predictive maintenance are monitored and analysed. According to this analysis, an action plan is taken. Preventive maintenance is based on historical data, averages, and expected life statistics to predict when maintenance activities will be required. Preventive maintenance refers to the repair or replacement of defective, broken, or worn equipment.
What innovation does Artesis offer for predictive maintenance?
Artesis’ unique patented technology utilizes a model-based voltage and current system approach to detect a wide range of faults on electric motors. This model-based approach works on the principle that the current drawn by an electric motor is affected by not only the applied voltage but also the behaviour of both the motor and the driven equipment.
Can Artesis predictive maintenance technology be used in hazardous areas?
Artesis predictive maintenance technology uses the motor as a sensor, without using any sensor. By measuring only current and voltage, both electrical and mechanical failures are detected months in advance. Thus, Artesis predictive maintenance solutions are the first choice in hard-to-reach and hazardous areas.
Does using Artesis predictive maintenance technology require expertise?
No. Analysing and interpreting data is not easy with other predictive maintenance technologies. Artesis does not make you bother with complex reports with its user-friendly interface. It is very easy to commission the system and start collecting data.


