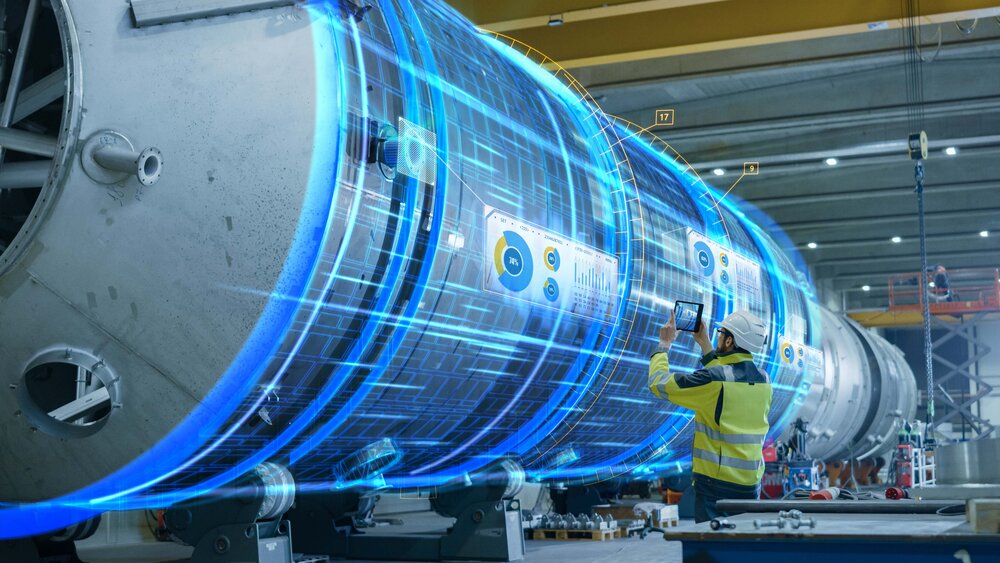
Maintenance 4.0: Scale the reliability
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, is a mind-boggling trend of automation and data interconnection that has taken the world by storm. It includes Internet of Things (IIoT), Wireless Sensors, Cloud Computing, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Big Data. The primary goal of Industry 4.0 is to connect machines, operators and processes through technology. Smart factories are equipped with advanced equipment, robotics and embedded software that collect and analyze data to ensure better decision making. When the data obtained from manufacturing operations are combined with operational data coming from ERP, supply chain, customer service and other corporate systems, even higher value can be created, with new levels of visibility and insight from previously siloed information.
This leads to increased automation, predictive maintenance, self-optimization of process improvements and most of all, a new efficiency and traceability which was not possible before. Maintenance is made easy by industry 4.0 solutions. We can quickly identify the source of failures using sensors, IIoT, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and other smart systems. It is possible to find the best preventive maintenance plan to find out which equipment is being affected, how these issues can hinder productivity and to prevent failures. Maintenance processes transform from a preventive model to a predictive model, shifting the emphasis from prevention to prediction. For instance, taking advantage of Big Data together with Artificial Intelligence allows us to correctly determine the useful life of the equipment, its risk of failure and the corresponding impact on the system.

With this said, let’s examine the key components that make up a successful predictive maintenance system:
Preventive Maintenance
We’ve all heard the saying “Prevention is better than cure”! Preventive maintenance quite simply prevents the failures in assets and equipment before they occur. Such maintenance is carried out in periodic intervals to ensure the uninterrupted operation and safety of the assets, even when the assets do not display any signs of damage.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a technique that utilizes data analysis tools and methods to identify anomalies in your operations and potential faults in your equipment and processes. In this way, you can rectify these errors before they can cause a failure.
In short, predictive maintenance uses historical and real-time data coming from various parts of your operation in order to predict issues before they occur. Predictive maintenance provides a series of important advantages such as increased return on investment, reduced cost of maintenance, fewer failures and less downtime.

Big data
Big Data refers to the large volume of configured and unconfigured data, which is collected during the production process. Big Data Analytics can help you unlock valuable insights that will allow to you make better business decisions.
Artificial intelligence
The goal of artificial intelligence in predictive maintenance is easy: to quickly analyze a large volume of real-time data to intelligently predict asset failures, this way manufacturers can keep their critical assets operational at the highest performance level.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Internet of Things has a profound impact on the manufacturing sector, leading to increased automation, more efficient operations and the creation of valuable new business models. While the implementation of digital technologies can lead to benefits across the supply chain, arguably the most significant impact can be gained in the field of predictive maintenance.
The use of data analysis means that companies would be able to identify patterns in their equipment status and performance, thereby correctly predicting when a failure might occur. Such foresight would lead to significant benefits in productivity by eliminating unplanned downtime.

Cloud computing
Cloud computing means the provision of data processing services, including servers, storage, databases, network, software, analytics and intelligence over the internet (cloud). It enables you to effectively obtain, collect, process and display the data coming from the equipment.