
The industrial market has seen growth in the condition monitoring of motors and generators. This is due to the increased reliability and availability of technology, which has provided a competitive advantage for buyers. Condition monitoring is an important part of maintaining a healthy plant. It is estimated that equipment breakdowns account for about 30% of downtime in manufacturing plants. This downtime costs businesses millions of dollars every year and can potentially harm company reputation. The best way to prevent these time-consuming breakdowns is to monitor your equipment for any signs of potential malfunctions. This article discusses what condition monitoring is, where it is used and how it differs from predictive maintenance.
Contents
What is Condition Monitoring?
Condition monitoring is a process that monitors or tests machinery or equipment during its operation. The goal is to identify potential failures before they happen. In addition to noticing when something is wrong, it can also help you know when something needs to be fixed or replaced. Condition monitoring can increase reliability, availability, and uptime for machines and equipment by reducing downtime.

Condition monitoring is used for many different applications in the industrial world, from motors and generators to wind turbines and solar panels. Monitoring devices help identify problems before they occur. They also provide remote access to critical information to alert people to an issue before it gets worse. However, it can be overwhelming to choose the right condition monitoring solution for your needs. There are many solutions on the market today.
The Effectiveness of Condition Monitoring In Preventing Unplanned Downtimes
Condition monitoring is one of the most effective and advanced methods of preventing unplanned downtimes in factories. The generator makes it possible to fulfill the power requirements in the modern era, and generator types and ratings vary concerning its use, location, and economics. Besides, the motor role is inevitable in the feasible operations of any industry. On top of that, it is an integral part of the processes such as power generation, oil & gas, cement, food processing, and fertilizer sector. Its use varies across the industry, and motor ratings start from a few watts to megawatts depending upon the nature of work. In mega industries, generators and heavy-duty motors must work under high loads and operates non-stop 24/7. As a result, we require reliable monitoring systems to oversee the nonstop functioning of motors and generators. In this post, we look at what condition monitoring is, why it’s necessary, and which approaches are best for it.
On top of that, it is an integral part of the processes such as power generation, oil & gas, cement, food processing, and fertilizer sector. Its use varies across the industry, and motor ratings start from a few watts to megawatts depending upon the nature of work. In mega industries, generators and heavy-duty motors must work under high loads and operates non-stop 24/7. Therefore, To manage the non-stop operation of motors and generators, we need to have reliable monitoring systems. Here, we discuss in detail what condition monitoring is, why it is important, and which methods are preferred in condition monitoring.
In mega industries, generators and heavy-duty motors must work under high loads and operates non-stop 24/7.
Due to non-stop usage of the motors and generators, wear and tear in parts are common abnormalities that need to be addressed. To predict and prevent massive failure of equipment is a vital need for today’s industry.
Condition Monitoring System

The first basic rule is to apply the pro-active approach to maintenance. The pro-active maintenance applies with physical inspection and with the help of performing periodic maintenance to determine any damaged or defective parts. Accordingly, the inadequate parts will be replaced before a major breakdown happens. It’s a little risky because periodic maintenance is planned as per the time specified, but over time, the generator and motor’s part’s condition remain deteriorated.
More Interested: Predictive Maintenance And Asset Management
So, what’s the solution?
The absolute solution comes up with comprehensive condition monitoring.
Condition Monitoring Techniques
Condition monitoring can perform 2 different methods, online and offline. However, nowadays, with the rapid rise of digitalization, online condition monitoring methods are preferred. In the online status monitoring method, critical equipment to be monitored is constantly monitored by cloud and IoT-based software. In this way, unplanned downtime that may occur are caught at the initial stage.
From past to present, there are many condition monitoring techniques such as oil analysis, acoustic emission, vibration analysis, thermography. One method can have advantages and disadvantages over the other. However, the use of these traditional methods is gradually decreasing, especially with the use of digitalization and IoT. Moreover, the significant decrease in the costs of sensors in the last 10 years and the emerging concept of big data push businesses to more digital solutions.
Artesis condition monitoring method has a significant advantage over other techniques. This innovative method, which does not require any sensors, can diagnose malfunctions that may occur in motors 6 months in advance by only obtaining current and voltage information. Since this technique does not require a sensor, it is an effective solution for monitoring rotating equipment in hazardous and hard-to-access areas. Artesis offers solutions in a wide range from chemical industry to ATEX fields, from oil and gas industry to water treatment plants.
Condition Monitoring Solutions
Condition monitoring is an advancement to know the health, safety, and performance of generators and motors where reliable, continuous, and efficient operations are required. There are two types of monitoring systems, the first one is offline monitoring and the second one is an online monitoring system. In this monitoring technique, different parameters are measured, transmitted, and monitored in the control station where the operator is aware of the working conditions of the generator and motor.,

The condition monitoring system is more important for high rating generators which are connected to the national grid where continuous operation is required. Because any voltage or frequency fluctuation can cause a total blackout in the whole country in the worst scenario. For this reason generator frequency, current, voltage, MVAR, winding temperature, bearing temperature, bearing vibration, lube oil levels, lube oil pressure, etc. needs to be measured, watched, and monitored continuously. Similarly for heavy-duty motors, bearing temperature, vibration, and cooling oil /or mechanism; needs to be monitored continuously. Online condition monitoring system is used where sensors measure the desired readings, convert those reading into signals which are transmitted to dedicated software which displays the values in the graph, numeric and in the bar as per requirements.

Condition monitoring solutions are critical to the performance of your motors and generators. In many industries, these systems provide an early warning for potential breakdowns or failures before they happen. High-tech condition monitoring solutions help minimize downtime and maintenance costs. There are effective ways to find and choose the right solution for your needs that won’t break the bank.
Condition Monitoring Software
Condition monitoring for motors and generators is a crucial part of plant maintenance. Motor condition monitoring can help plant managers reduce the number of unscheduled shutdowns by using predictive analytics to pinpoint risks before they occur. With this technology, you will not have to wait until the motor fails before you get an indication that something is wrong. The condition of your motors and generators will be constantly monitored so that you can take proactive measures when it is needed. In addition, condition monitoring for motors and generators can also provide a way for companies to quantify the level of wear and tear on their equipment which is necessary for long-term asset management plans.
Whenever unplanned downtime occurs in a plant, it is never a good time. Even the simplest and smallest errors can bring down a plant’s productivity to a minimum, with a detrimental effect to the cost structure and profitability. A cost-cutting engineering team can go far in improving power generation and distribution by only minimally increasing the efficiency and output by using better methods and monitoring the condition of the equipment. For this reason, generators and motor must be in the best working condition at all times. This ensures that they function efficiently and produce maximum power. To monitor the condition of these machines, various electrical and mechanical monitoring methods are used.
Dont’ Miss:Failures In Pump And Predictive Maintenance
Therefore, the condition monitoring system is the backbone of the safe operation of the generator & motor, to save the process cost in terms of efficiency, planning maintenance schedules, increase equipment life, and save huge amounts in terms of tripping stoppage of process.
Types of Condition Based Monitoring
Such fault conditions are actually cascading effects of even a single abnormal condition. Presently, the reading data history will devise the mechanism when, how, and which parts need to be repaired or replaced. Just imagine, in case there is no condition monitoring system is there then the maintenance staff will come to know after generator or motor is partially completely damaged. It not only cost the price of equipment but also the major loss is the tripping of plant, in result no power electricity generation in case of the generator and for motor case, stoppage of production in process, cement, fertilizer industry.

The condition monitoring system is the backbone of the safe operation of the generator & motor.
Therefore; the condition monitoring system is the backbone of the safe operation of the generator & motor, to save the process cost in terms of efficiency, planning maintenance schedules, increase equipment life, and save huge amounts in terms of tripping stoppage of process.
Why Artesis e-PCM?
The Artesis e-PCM is an AI-based online condition monitoring system for wind turbines and generators. e-PCM uses patented technology to offer a unique solution that safeguards generators from electrical and mechanical faults. e-PCM continuously identifies existing and developing faults on generators and their prime movers, effectively using the generator itself as a sophisticated transducer.
e-PCM utilizes an intelligent, model-based approach to provide anomaly detection by measuring the current and voltage signals from the electrical supply from the generator. It is permanently mounted, generally in the generator control center, and is applicable to 3- phase AC generators. Accompanying Artesis Enterprise Server Software and IoT Portal are used to view the data. Our mission to help industrial and commercial plants maximize their efficiency and uptime. Companies need to make sure they have the right condition monitoring solutions for motors and generators to make sure that their equipment is running smoothly and efficiently. Today, it’s more critical than ever for businesses to monitor their assets for potential problems. With our custom-designed Condition Monitoring Solutions for Motors and Generators, you can eliminate production downtime caused by unexpected mechanical failures.
Please feel free to contact us if you have any queries related to condition monitoring for motor and generators. Our experts are always available to assist our esteemed clients with their queries.
Machine Condition Monitoring System
Monitoring the condition of machinery in a plant is one of the most important technologies for reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance at the right time. In line with the data received from the machines, electrical, mechanical and process failures will be determined in advance and the maintenance team will be informed; thus, there will be a chance to intervene while the malfunction is still in its initial stage. The following faults can be easily detected by machine condition monitoring.
- Stator fault
- Rotor fault
- Angular and parallel misalignment
- Broken, damaged and loose rotor bars
- Bearing fault
- Ball/roller wear
- Assembly phase problems
- Process Faults
Case Study
Sector: Waste Disposal Company: Waste Incineration, Recycling
Equipment: Fan Failure: Winding Failure
Figure 1 and 2 display the trends of current and active power parameters of 14V001 equipment which had failure on stator windings on 21 November 2014. On November 21, 2014, the equipment with failure was sent to rewind the stator winding and it was recommissioned on 22 November 2014. Until 25 November 2014, an increase was observed in the current drawn by the rewinding motor. The customer was asked whether the load of the motor was changed by the operator and learned that no changes were made to load. After detailed inspection, it was realised that there was an error in the rewinding process and equipment has drawn more current than expected. The equipment rewinding has replaced with spare motor and the current values were observed again.As can be seen on Figure 2, there was a decrease in current values. In the event that the equipment that was rewinding was operated in this condition, an energy loss of 61320 kWh / year would have occurred.
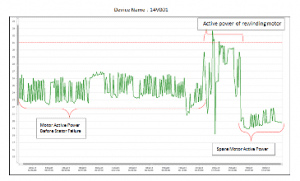
Figure 1: The trend of active power parameter of 14V001 Equipment
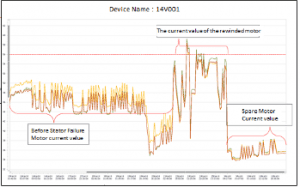
Figure 2: The trend of current parameter of 14V001 Equipment
Frequently Asked Questions for Condition Monitoring
What are condition monitoring techniques?
Motor current analysis, vibration analysis, infrared thermography, acoustic analysis are some common condition monitoring techniques.
What is the purpose of motor condition monitoring?
Rotating equipment and electric motors are devices with the highest electricity consumption. Thanks to the condition monitoring, the failures that may occur in the motors are predicted in advance and the failure is intervened months in advance. Condition monitoring both prevents unplanned downtime and highly provides energy efficiency. Moreover, unnecessary maintenance is prevented by motor condition monitoring.
What are the key benefits of motor condition monitoring?
The key benefits of motor condition motor monitoring is improved reliability, decreased replacement costs, reduced system downtime, improved spares management, increased maintainability.




 White Papers
White Papers Case Study
Case Study Documents
Documents Webinars
Webinars Events
Events ROI Calculator
ROI Calculator FAQ
FAQ